#Spring Boot Vs Spring MVC
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Why Java Is Still the King in 2025—and How Cyberinfomines Makes You Job-Ready with It

1. Java in 2025: Still Relevant, Still Dominating Despite the rise of new languages like Python, Go, and Rust, Java is far from dead—it’s actually thriving.
In 2025, Java powers:
40%+ of enterprise backend systems
90% of Android apps
Global banking & fintech infrastructures
E-commerce giants like Amazon, Flipkart & Alibaba
Microservices and cloud-native platforms using Spring Boot
Java is reliable, scalable, and highly in demand. But just learning syntax won’t get you hired. You need hands-on experience, framework expertise, and the ability to solve real-world problems.
That’s exactly what Cyberinfomines delivers.
2. The Problem: Why Most Java Learners Don’t Get Jobs Many students learn Java but still fail to land jobs. Why?
❌ They focus only on theory ❌ They memorize code, don’t build projects ❌ No real understanding of frameworks like Spring Boot ❌ Can’t explain their code in interviews ❌ Lack of problem-solving or debugging skills
That’s where Cyberinfomines’ Training changes the game—we teach Java like it’s used in real companies.
3. How Cyberinfomines Bridges the Gap At Cyberinfomines, we:
✅ Teach Core + Advanced Java with daily coding tasks ✅ Use real-world problem statements (not academic ones) ✅ Give exposure to tools like IntelliJ, Git, Maven ✅ Build full-stack projects using Spring Boot + MySQL ✅ Run mock interviews and HR prep ✅ Help you create a Java portfolio for recruiters
And yes—placement support is part of the package.
4. Java Course Curriculum: Built for the Real World Core Java
Data types, loops, arrays, OOP principles
Exception handling, packages, constructors
File handling & multithreading
Classes vs Interfaces
String manipulation & memory management
Advanced Java
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)
Servlet Lifecycle
JSP (Java Server Pages)
HTTP Requests & Responses
MVC Design Pattern
Spring Framework + Spring Boot
Dependency Injection & Beans
Spring Data JPA
RESTful API Creation
Security & authentication
Connecting with front-end apps (React/Angular)
Tools Covered
IntelliJ IDEA
Eclipse
Postman
Git & GitHub
MySQL & Hibernate
Live Projects
Library Management System
Employee Leave Tracker
E-Commerce REST API
Blog App with full CRUD
Interview Preparation
DSA using Java
Java-based coding problems
100+ mock interview questions
HR round preparation
Resume writing workshops
5. Who Should Learn Java in 2025? You should choose Java if you are:
A fresher who wants a strong foundation
A non-tech graduate looking to switch to IT
A teacher/trainer who wants to upskill
A professional aiming for backend roles
Someone interested in Android development
A student looking to crack placement drives or government IT jobs
6. Real Success Stories from Our Java Learners
Amit (BSc Graduate) – Now working as a Java backend developer at an IT firm in Pune. Built his confidence with live projects and mock tests.
Pooja (Mechanical Engineer) – Switched from core to IT after completing Cyberinfomines’ Java program. Cracked TCS with flying colors.
Rahul (Dropout) – Didn’t finish college but now works remotely as a freelance Spring Boot developer for a US-based startup.
Every story started with zero coding experience. They ended with real jobs.
7. Top Java Careers in 2025 & Salary Trends In-demand roles include:
Java Backend Developer
Full Stack Developer (Java + React)
Android Developer (Java)
Spring Boot Microservices Architect
QA Automation with Java + Selenium
API Developer (Spring + REST)
Starting salary: ₹4.5 – ₹8 LPA (for freshers with strong skills) Mid-level: ₹10 – ₹20 LPA Freelancers: ₹1,000 – ₹2,500/hour
Java is stable, scalable, and pays well.
8. Certifications, Tools & Practical Add-Ons After training, you’ll earn:
Cyberinfomines Java Developer Certificate
Portfolio with at least 3 GitHub-hosted projects
Proficiency in IntelliJ, Maven, Git, MySQL
Resume aligned with Java job descriptions
Interview recordings and performance feedback
9. What Makes Cyberinfomines Java Training Different
✔ Human mentorship, not just videos ✔ Doubt sessions + code reviews ✔ Classes in Hindi & English ✔ Live assignments + evaluation ✔ Placement-oriented approach ✔ No-nonsense teaching. Only what’s needed for jobs.
We focus on you becoming employable, not just completing a course.
10. Final Words: Code Your Future with Confidence Java in 2025 isn’t just relevant—it’s crucial.
And with Cyberinfomines, you don’t just learn Java.
You learn how to:
Solve real problems
Write clean, scalable code
Work like a developer
Get hired faster
Whether you’re starting fresh or switching paths, our Java course gives you the skills and confidence you need to build a future-proof career.
📞 Have questions? Want to get started?
Contact us today: 📧 [email protected] 📞 +91-8587000904-905, 9643424141 🌐 Visit: www.cyberinfomines.com
0 notes
Text
Essential Full Stack Development Interview Questions to Prepare For Your Next Job Opportunity
The demand for skilled full stack developers continues to grow as more companies seek professionals who can handle both the front-end and back-end development of applications. Preparing for a full stack development interview involves understanding a wide range of concepts that cover various technologies, frameworks, and programming practices.
To set yourself apart and confidently face interviews, consider exploring these essential full stack development interview questions. And for an insightful video overview of full stack interview preparation, check out this Full Stack Developer Interview Preparation Guide.
1. What is Full Stack Development?
Full stack development refers to the practice of working on both the front-end (client-side) and back-end (server-side) of a web application. A full stack developer is proficient in multiple technologies that enable them to build fully functional web applications from start to finish.
Key Points to Discuss:
Differences between front-end, back-end, and full stack development.
Advantages of hiring a full stack developer for a project.
2. What Are the Most Commonly Used Front-End Technologies?
Front-end development involves creating the user interface and ensuring a seamless user experience. The most popular front-end technologies include:
HTML: The standard markup language for creating web pages.
CSS: Used to style and layout web pages.
JavaScript: Essential for interactive features.
Frameworks/Libraries: React, Angular, and Vue.js.
Follow-Up Questions:
How do these technologies differ in terms of use cases?
Can you explain the benefits of using a front-end framework like React over vanilla JavaScript?
3. Explain the Role of Back-End Technologies in Full Stack Development.
The back-end of an application handles the server, database, and business logic. Key technologies include:
Node.js: A JavaScript runtime for server-side programming.
Express.js: A web application framework for Node.js.
Databases: SQL (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL) and NoSQL (e.g., MongoDB).
Other Languages: Python (Django, Flask), Ruby (Rails), and Java (Spring Boot).
Important Discussion Points:
RESTful services and APIs.
Authentication and authorization mechanisms (e.g., JWT, OAuth).
4. How Do You Ensure Code Quality and Maintainability?
Interviewers often ask this question to understand your approach to writing clean, maintainable code. Emphasize:
Version Control: Using Git and platforms like GitHub for collaborative coding.
Linting Tools: ESLint for JavaScript and other language-specific tools.
Code Reviews: The importance of peer reviews for improving code quality.
Best Practices: Following design patterns and SOLID principles.
5. Can You Discuss the MVC Architecture?
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture is a common design pattern used in full stack development. Each part of the pattern has a distinct role:
Model: Manages data and business logic.
View: The user interface.
Controller: Connects the Model and View, handling input and output.
Why It’s Important:
Helps organize code, making it more scalable and easier to maintain.
Many frameworks, such as Django and Ruby on Rails, are built on MVC principles.
6. What Is REST and How Is It Used in Full Stack Development?
Representational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style used to design networked applications:
Key Features: Stateless, cacheable, and uses standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
Implementation: Building RESTful APIs to enable communication between client and server.
Common Follow-Ups:
How do RESTful APIs differ from GraphQL?
Can you provide an example of designing a RESTful API?
7. Explain the Role of Databases and When to Use SQL vs. NoSQL.
Choosing between SQL and NoSQL depends on the application's needs:
SQL Databases: Structured, table-based databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL. Best for applications requiring complex queries and data integrity.
NoSQL Databases: Flexible, schema-less options like MongoDB and Cassandra. Ideal for handling large volumes of unstructured data.
Typical Questions:
What are the ACID properties in SQL databases?
When would you prefer MongoDB over a relational database?
8. How Do You Implement User Authentication?
User authentication is crucial for any secure application. Discuss:
Methods: Sessions, cookies, JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
Frameworks: Passport.js for Node.js, Auth0 for advanced solutions.
Best Practices: Storing passwords securely using hashing algorithms like bcrypt.
9. What Are Webpack and Babel Used For?
These tools are essential for modern JavaScript development:
Webpack: A module bundler for bundling JavaScript files and assets.
Babel: A JavaScript compiler that allows you to use next-gen JavaScript features by transpiling code to be compatible with older browsers.
Related Questions:
How do you optimize your build for production using Webpack?
What is tree shaking, and how does it improve performance?
10. How Do You Handle Error Handling in JavaScript?
Error handling is vital for ensuring that applications are resilient:
Try-Catch Blocks: For handling synchronous errors.
Promises and .catch(): For managing asynchronous operations.
Error Handling Middleware: Used in Express.js for centralized error management.
Important Concepts:
Logging errors and using tools like Sentry for real-time monitoring.
Creating user-friendly error messages.
Preparing thoroughly for full stack development interviews by understanding these questions will set you on the path to success. For a comprehensive walkthrough and additional insights, make sure to check out this YouTube guide, where these topics are discussed in detail to boost your interview readiness.
0 notes
Text
Top Full Stack Developer Interview Questions (2024)

In the dynamic landscape of technology, Full Stack Development has emerged as a crucial field, demanding professionals with a diverse skill set and a deep understanding of both frontend and backend technologies. As companies continue to embrace digital transformation, the demand for skilled Full Stack Developers remains high. This article delves into the top Full Stack Developer interview questions for 2024, focusing on the Java Full Stack roadmap and Python Full Stack syllabus.
Introduction to Full Stack Development
Full stack development refers to the practice of working on both the front end and back end of a web application or software. A full stack developer is someone who is proficient in working with both the client-side and server-side technologies, allowing them to handle all aspects of the development process.
In a typical full stack development scenario, the front end involves creating the user interface and user experience (UI/UX) of the application. This includes designing and developing components such as web pages, forms, buttons, navigation menus, and interactive elements using technologies like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and front-end frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js.
On the other hand, the back end involves working with the server-side logic, databases, and server management. This includes tasks such as handling user authentication, processing data, managing server requests, and interacting with databases to store and retrieve information. Technologies commonly used in back-end development include programming languages like Node.js, Python, Java, or PHP, along with frameworks like Express.js, Django, Spring Boot, or Laravel.
Full stack developers are required to have a diverse skill set that encompasses both front-end and back-end technologies. They need to understand how to integrate these technologies seamlessly to build fully functional and responsive web applications. Additionally, they should be familiar with version control systems like Git, deployment processes, and have a good grasp of software development principles and best practices.
Overall, full stack development offers a holistic approach to building web applications, allowing developers to work on all layers of the software stack and deliver end-to-end solutions that meet user requirements effectively.
Top Interview Questions for Full Stack Developers

Technical Questions
Sure, here are some top interview questions for full-stack developers:
Frontend Development:
What are the key differences between HTML, CSS, and JavaScript?
Explain the box model in CSS and how it affects layout.
What is responsive web design, and how do you ensure your web applications are responsive?
How do you optimize website performance, both in terms of loading speed and user experience?
What are CSS preprocessors like Sass or Less, and why would you use them?
Backend Development:
What is the difference between server-side scripting and client-side scripting?
Explain the role of databases in web development and discuss different types of databases you are familiar with.
What is RESTful API, and how do you design and consume RESTful APIs?
How do you handle authentication and authorization in a web application?
Discuss the importance of caching in backend development and some popular caching strategies.
Full-Stack Development:
What is the MEAN (MongoDB, Express.js, AngularJS, Node.js) stack, and how does it differ from the MERN (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) stack?
Explain the concept of MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture and how it's implemented in web development.
How do you handle state management in a single-page application (SPA)?
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of monolithic vs microservices architecture for web applications.
What tools and technologies do you use for version control, continuous integration, and deployment?
Problem-Solving:
Given a scenario, how would you approach debugging a frontend/backend issue in a web application?
Describe a challenging project you worked on and how you overcame technical obstacles during its development.
Implement a simple algorithm (e.g., reverse a string, find the largest number in an array) using a programming language of your choice.
How do you ensure code quality and maintainability in a collaborative development environment?
Discuss your experience with testing methodologies such as unit testing, integration testing, and end-to-end testing.
Soft Skills and Communication:
How do you prioritize tasks and manage your time effectively when working on multiple projects or tasks simultaneously?
Describe a situation where you had to work in a team and resolve conflicts or disagreements effectively.
How do you stay updated with the latest trends and technologies in web development?
Explain a complex technical concept to a non-technical stakeholder or client.
Discuss a project where you had to quickly learn a new technology or framework and how you approached the learning process.
These questions cover a range of topics and skills that are important for full-stack developers, including technical knowledge, problem-solving abilities, communication skills, and project management experience. Adjust the complexity of the questions based on the seniority level of the position you are hiring for.
Behavioral Questions
Certainly, here are some behavioral questions tailored for full-stack developers:
Adaptability and Learning:
Describe a time when you had to quickly learn a new technology or programming language for a project. How did you approach the learning process, and what was the outcome?
Can you give an example of a challenging technical problem you faced and how you overcame it through self-directed learning or seeking help from others?
Problem-Solving and Decision Making:
Walk me through a complex issue you encountered during a project. How did you analyze the problem, identify possible solutions, and make a decision on the best course of action?
Describe a situation where you had to prioritize tasks or features in a project with tight deadlines. How did you decide what to focus on first, and what was the result?
Collaboration and Communication:
Discuss a project where you worked closely with a team of developers, designers, or other stakeholders. How did you ensure effective communication and collaboration among team members?
Can you share an example of a time when you had to present technical information or solutions to non-technical stakeholders? How did you ensure they understood the key points?
Handling Challenges and Failures:
Describe a project or task that didn't go as planned. What challenges did you face, and how did you handle the situation? What did you learn from the experience?
Have you ever made a mistake in your code that caused a significant issue? How did you identify and rectify the error, and what steps did you take to prevent similar mistakes in the future?
Leadership and Initiative:
Have you ever taken the lead on a project or initiative? What was your role, and how did you ensure the project's success?
Describe a time when you proposed an innovative solution or improvement to an existing process or technology. How was your idea received, and what was the outcome?
These behavioral questions focus on the candidate's ability to adapt, solve problems, collaborate effectively, learn from challenges, and take initiative. They provide insights into the candidate's past experiences and behaviors, which can help assess their fit for the role and the team dynamics.
Java Full Stack Developer Interview Questions

Sure, here are some Java Full Stack Developer interview questions:
What is the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM?
Explain the concept of object-oriented programming and its key principles.
What is a servlet? How does it differ from an applet?
What is JDBC? How do you connect Java applications to databases using JDBC?
Can you explain the Spring framework and its core features?
What is RESTful web services? How do you implement RESTful APIs in Java?
Explain the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture and its advantages in web development.
What are some commonly used design patterns in Java? Provide examples.
How do you handle transactions in a Java application? Discuss the transaction management options.
What tools and technologies do you use for front-end development in a Java Full Stack environment?
Can you explain the concept of microservices architecture? How does it differ from monolithic architecture?
How do you ensure security in a Java web application? Discuss some best practices.
What is Docker, and how do you use it in Java application deployment?
Discuss the differences between SOAP and RESTful web services.
Can you explain the concept of dependency injection and how it is implemented in Spring?
These questions cover a range of topics typically encountered in Java Full Stack Developer interviews. Candidates should be able to demonstrate their understanding of Java programming, web development concepts, frameworks like Spring, and related technologies.
Python Full Stack Developer Interview Questions

Certainly! Here are some Python Full Stack Developer interview questions:
What is the difference between Python 2 and Python 3? Why should we use Python 3 for new projects?
Explain the concept of virtual environments in Python and why they are useful.
How does Flask differ from Django? When would you choose one over the other for a web development project?
What is ORM (Object-Relational Mapping)? Provide an example of an ORM library used in Python.
Describe the process of deploying a Flask or Django application to a production server.
What are decorators in Python? How can decorators be used in web development?
Explain the role of WSGI (Web Server Gateway Interface) in Python web applications.
What is RESTful API? How would you design and implement a RESTful API using Python?
Discuss the importance of testing in software development. What are some popular testing frameworks used in Python?
How do you handle database migrations in Django or Flask applications?
Describe the difference between synchronous and asynchronous programming. When would you choose asynchronous programming in Python?
What are some strategies for optimizing the performance of a Python web application?
Discuss the security considerations you would take into account when developing a web application in Python.
Have you worked with any cloud platforms for deploying Python applications? If so, which ones and what was your experience?
Can you explain the concept of caching in web development? How would you implement caching in a Python-based web application?
These questions cover a range of topics relevant to python full stack syllabus , including web frameworks, databases, testing, optimization, security, and deployment. Adjust the complexity of the questions based on the candidate's level of experience.
Tips for Acing Full Stack Developer Interviews
Review and practice coding exercises related to data structures, algorithms, and design patterns.
Showcase your portfolio projects and highlight your contributions and problem-solving skills.
Prepare for behavioral questions by reflecting on past experiences and achievements.
Stay updated with the latest trends and technologies in Full Stack Development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Full Stack Developer interviews in 2024 require a comprehensive understanding of various technologies, from core programming languages to advanced frameworks and tools. By preparing diligently and showcasing your skills and experiences effectively, you can increase your chances of landing a rewarding Full Stack Developer role.
FAQs
What is the role of a Full Stack Developer? A Full Stack Developer is responsible for designing, developing, and maintaining web applications, handling both frontend and backend aspects of the software.Which programming languages are essential for Full Stack Development? Key languages include JavaScript, Python, Java, and frameworks such as React, Angular, Spring Boot, and Django.How can I improve my skills as a Full Stack Developer? Practice coding regularly, work on real-world projects, stay updated with industry trends, and participate in online communities and forums.What are some common challenges faced by Full Stack Developers? Challenges may include managing diverse technologies, ensuring scalability and performance, and staying updated with rapid technological advancements.What opportunities does Full Stack Development offer in the job market? Full Stack Developers are in high demand across industries, offering lucrative career prospects and opportunities for growth and innovation.
and innovation.
0 notes
Text
Head-to-Head: PHP vs. Java - Which Language Reigns Supreme?

Head-to-Head: PHP vs. Java - Which Language Reigns Supreme? The debate between PHP and Java has long been a topic of discussion among developers, with proponents of each language advocating for its superiority in various aspects of web development, enterprise applications, and system architecture. In this head-to-head comparison, we'll delve into the strengths, weaknesses, and use cases of PHP and Java to determine which language reigns supreme in the world of software development.
Overview of PHP:
PHP, initially created as a server-side scripting language for web development, has gained widespread popularity for its simplicity, flexibility, and ease of use. Here are some key considerations regarding PHP:
Simplicity and Ease of Use:
PHP is renowned for its straightforward syntax and easy learning curve, making it accessible to beginners and experienced developers alike.
Its scripting nature allows developers to embed PHP code directly into HTML, enabling dynamic content generation and server-side processing.
Web Development Focus:
PHP is primarily designed for web development, with built-in features for processing form data, interacting with databases, and generating dynamic web pages.
It integrates seamlessly with popular web servers like Apache and Nginx and databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite.
Vibrant Ecosystem:
PHP boasts a vibrant ecosystem of frameworks, libraries, and tools that streamline web development tasks and accelerate project delivery.
Frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter provide robust MVC architecture, routing, ORM, and other features for building scalable and maintainable web applications.
Overview of Java:
Java, renowned for its platform independence, scalability, and robustness, is widely used for building enterprise-grade applications, backend systems, and large-scale distributed systems. Here are some key considerations regarding Java:
Write Once, Run Anywhere (WORA):
Java's WORA principle enables developers to write code once and run it on any platform that supports Java, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and various mobile devices.
This platform independence is achieved through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which provides a consistent runtime environment for Java applications.
Scalability and Performance:
Java offers scalability and performance advantages, making it suitable for building large-scale enterprise applications that can handle high volumes of concurrent users and transactions.
Its robust type system, memory management features, and multithreading support contribute to improved application performance and responsiveness.
Enterprise Integration:
Java's extensive ecosystem and enterprise-grade features make it well-suited for integrating with existing systems, middleware, and enterprise solutions.
Frameworks like Spring Boot, Jakarta EE (formerly Java EE), and Apache Camel provide comprehensive support for building enterprise applications, RESTful APIs, and microservices.
Head-to-Head Comparison:
Performance:
Java generally offers better performance and scalability compared to PHP, especially for large-scale enterprise applications and systems with high concurrency requirements.
PHP's performance has improved over the years, but it may still lag behind Java in terms of raw processing power and efficiency.
Developer Productivity:
PHP's simplicity and ease of use contribute to faster development cycles and rapid prototyping, making it suitable for small to medium-sized web projects.
Java's verbose syntax and boilerplate code may require more time and effort upfront but can lead to more maintainable and scalable codebases over the long term.
Ecosystem and Tooling:
PHP has a robust ecosystem of frameworks, libraries, and tools tailored for web development, with a focus on simplicity, flexibility, and ease of use.
Java's ecosystem is broader and more diverse, catering to a wide range of use cases, including web development, enterprise integration, mobile development, and big data processing.
Use Cases and Project Requirements:
The choice between PHP and Java ultimately depends on the specific requirements, scalability needs, and performance considerations of the project at hand.
PHP may be a better fit for small to medium-sized web projects, startups, and rapid prototyping, while Java shines in large-scale enterprise applications, middleware, and mission-critical systems.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, both PHP and Java have their strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of projects and development scenarios. While PHP excels in simplicity, ease of use, and rapid development, Java boasts scalability, performance, and enterprise-grade features. The choice between PHP and Java should be based on the specific requirements, project goals, and scalability needs of the application, ensuring that developers choose the language that best aligns with their project's objectives and long-term vision. Ultimately, the language that reigns supreme depends on the context of the project and the priorities of the development team.
#software engineering#Php Vs Java#application development#app development#mobile app development#programming
0 notes
Text
CHEAT SHEET TO
FULL STACK SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT (IN 21 WEEKS)

Below is a more extended schedule to cover all the topics we've listed for approximately 2-3 months. This schedule assumes spending a few days on each major topic and sub-topic for a comprehensive understanding. Adjust the pace based on your comfort and learning progress:
Week 1-2: Introduction to Programming – Python
- Programming Structure and Basic Principles
- Programming Constructs - Loops, Functions, Arrays, etc.
Week 3: Git and Version Control
- Git Basics
- Collaborative Git Workflow
Week 4: HTML and CSS
- HTML Basics
- CSS Styling and Layout
Week 5: Object-Oriented Programming - Python
- Object-Oriented Paradigms
- Exception Handling, Collections
Week 6: Data Structures - Linear Data Structures
- Arrays, Strings, Stacks, Queues
- Linked Lists
Week 7: Data Structures - Binary Trees and Tree Traversals
- Binary Trees and Binary Search Trees
- Tree Traversal Algorithms
Week 8: Algorithms - Basic Algorithms and Analysis
- Recursion
- Searching and Sorting Algorithms
- Algorithm Analysis
Week 9: Algorithms - Advanced Algorithms and Evaluation
- Greedy Algorithms
- Graph Algorithms
- Dynamic Programming
- Hashing
Week 10: Database Design & Systems
- Data Models
- SQL Queries
- Database Normalization
- JDBC
Week 11-12: Server-Side Development & Frameworks
- Spring MVC Architecture
- Backend Development with Spring Boot
- ORM & Hibernate
- REST APIs
Week 13: Front End Development - HTML & CSS (Review)
- HTML & CSS Interaction
- Advanced CSS Techniques
Week 14-15: Front-End Development - JavaScript
- JavaScript Fundamentals
- DOM Manipulation
- JSON, AJAX, Event Handling
Week 16: JavaScript Frameworks - React
- Introduction to React
- React Router
- Building Components and SPAs
Week 17: Linux Essentials
- Introduction to Linux OS
- File Structure
- Basic Shell Scripting
Week 18: Cloud Foundations & Containers
- Cloud Service Models and Deployment Models
- Virtual Machines vs. Containers
- Introduction to Containers (Docker)
Week 19-20: AWS Core and Advanced Services
- AWS Organization & IAM
- Compute, Storage, Network
- Database Services (RDS, DynamoDB)
- PaaS - Elastic BeanStalk, CaaS - Elastic Container Service
- Monitoring & Logging - AWS CloudWatch, CloudTrail
- Notifications - SNS, SES, Billing & Account Management
Week 21: DevOps on AWS
- Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment
- Deployment Pipeline (e.g., AWS CodePipeline, CodeCommit, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy)
- Infrastructure as Code (Terraform, CloudFormation)
Please adjust the schedule based on your individual learning pace and availability. Additionally, feel free to spend more time on topics that particularly interest you or align with your career goals. Practical projects and hands-on exercises will greatly enhance your understanding of these topics.



0 notes
Photo

Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC vs. Spring: How Do They Compare? ☞ http://on.geeklearn.net/3a6c6f1288 #SpringBoot #SpringMVC #Spring
#Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC vs. Spring#Spring Boot#Spring MVC#Spring#Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC#Spring Boot vs. Spring#Spring MVC vs. Spring
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC vs. Spring: How Do They Compare? ☞ http://on.geeklearn.net/3a6c6f1288 #SpringBoot #SpringMVC #Spring
#Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC vs. Spring#Spring Boot#Spring MVC#Spring#Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC#Spring Boot vs. Spring#Spring MVC vs. Spring
2 notes
·
View notes
Photo

Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC vs. Spring: How Do They Compare? ☞ http://on.geeklearn.net/3a6c6f1288 #SpringBoot #SpringMVC #Spring
#Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC vs. Spring#Spring Boot#Spring MVC#Spring#Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC#Spring Boot vs. Spring#Spring MVC vs. Spring
0 notes
Photo

Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC vs. Spring: How Do They Compare? ☞ http://on.geeklearn.net/3a6c6f1288 #SpringBoot #SpringMVC #Spring
#Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC vs. Spring#Spring Boot#Spring MVC#Spring#Spring Boot vs. Spring MVC#Spring Boot vs. Spring#Spring MVC vs. Spring
0 notes
Text
How To Become A Full Stack Developer In Ninety Days
We at 360DigiTMG give our students the choice of each classroom and online studying. There are many initiatives that one can take up in this subject to realize sensible knowledge. You can work on constructing a web software for actual estate, storage options, mobile tracking, reporting tool software, or a wholesale distribution system that provides sooner inquiries to the monetary information. It will assist you to grasp MongoDB installation, knowledge modelling, schema design, knowledge indexing, monitoring, sharding, replication and aggregation.
Handle diverse data varieties and handle your purposes effectively using MongoDB. Brush up on your knowledge of software development fundamentals, Agile and Scrum methodologies, Java and information structures, GIT to manage version control systems, and Maven to handle project dependencies. This Full Stack Java developer course in Kuala Lumpur will allow you to increase your Full-Stack Developer occupation. To design highly net-scalable packages, you may research prime business expertise with a Full Stack Java developer course in Kuala Lumpur together with Servlets, Hibernate, Spring Boot, Angular, and JSPs, as well as MVC, web services, and SOA.
They will help you in gaining the maximum profit out of this net growth certification program and help you understand your full potential. A certificate in the skilled world right now, the best method for you to prove your experience in any area. It most frequently acts as an entry point for you to get entry to nice job alternatives to showcase your skills and get the credit score you deserve. This is particularly true in web improvement as well, with the wide range of languages and instruments which are used at present. The greatest contributors include medicines, medical tools, smelting, lumber, wood pulp, Islamic finance, petroleum, and liquefied natural fuel.
Whether you are an skilled skilled working in the IT industry, or an aspirant planning to enter the world of full-stack internet improvement, This Program is designed and developed to accommodate numerous professional backgrounds. This module will help college students in designing and developing powerful modern net applications that type the base for the apps, websites, and techniques that businesses use daily. The training commences with teaching you the way to code net apps with spectacular designs and possess the data to implement dynamic HTML results using some cool tags. Each module consists of multiple technologies that will help you acquire more expertise and discover completely different applied sciences and frameworks at Frontend at backend and Database (NoSQL-MongoDB).
All these firms provide significant development opportunities solely if you have a full stack java developer certification in Kuala Lumpur. Full-stack java developers ought to try to achieve certifications for the abilities they need to master. Some of them embody Angular coaching, Python Fundamentals, Node.JS course, and Selenium coaching course.
You’ll be guided step-by-step right from the basics to the superior subjects. AI has turn into an integral part of net development at the enterprise level. With Chatbots attending to queries by way of text and voices and minimizing the prices by half has revolutionized customer expertise.
Still, I personally discovered Max'sThe Complete Angular Guide programs most fun and useful and highly recommend to anybody who wants to study Angular in-depth and in a quick time. By introducing features like auto-configuration and Starter dependencies, Spring Boot alleviates the ache of Java developers who spend lots of time configuring Spring and finding a set of compatible libraries to work collectively. Though there isn't a ultimate verdict on React vs. Angular battle yet, going with the pattern, it is more and more wanting that React is going to win this epic war.
The Full-Stack Web Developer Certificate is your badge of recognition. Display your certificate and earn appreciation from office colleagues and business friends.
Back-end languages and frameworks corresponding to Express, Node.js, Python, Django, and so forth., for creating functions. Detailed directions in entrance-finish development, which lets you create rich and engaging person interfaces, in addition to server-aspect improvement, which lets you create powerful and scalable websites and back-finish APIs. With a structured curriculum and business veterans as instructors, Scaler Academy is leaving no stone unturned to make skilled internet builders out of every applicant. As we understand what's the gist of full stack developer programs and what we should aspire to anticipate from them, we transfer forward to deliver you the record of 15 best full stack developer programs to help you obtain your best. Oracle, SQL, NoSQL, and MongoDB are the database frameworks one must be skilled at, along with cloud computing. FULL STACK DEVELOPMENT is a talent related to those that can work with website growth, net software improvement and operations of a website.
Explore more on - full stack developer course with placement
https://360digitmg.com/course/certification-program-on-full-stack-web-developer
INNODATATICS SDN BHD (1265527-M)
360DigiTMG - Data Science, IR 4.0, AI, Machine Learning Training in Malaysia
Level 16, 1 Sentral, Jalan Stesen Sentral 5, KL Sentral, 50740, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
+ 601 9383 1378 / + 603 2092 9488
#full stack development course#full stack developer course#full stack web development course malaysia
0 notes
Text
List of tools to become a java full-stack developer

There are a ton of full-stack developer tools. From IDEs to mission administration apps, you’ll locate a plethora of alternatives to select from. That’s why it can get a little difficult for a developer. As the demand for full-stack builders will increase so does the wide variety of tools.
Read More: java full stack online course
With so many selections around, you can’t simply be counted on trial and error and see which device works with you and which doesn’t. You’ll give up losing a lot of your time and power this way, and you may now not even discover the device you needed.
To assist you in that regard, we have come up with a listing of the satisfactory full-stack developer equipment in the market. Some of this equipment is broadly popular, and some aren’t. But all of them make improvement extra on hand and extra efficient.
So, in addition to ado, let’s get started.
Who is a Full-Stack Developer?
The easiest way to outline a full-stack developer is “a candidate who can improve each customer and server software”. If a developer works on full-stack, it implies that he/she is performing all the duties related to Front-end, Back-end, the database, and ultimately the integration process. As a full-stack developer, you need to care about coding the server-side API, programming languages for again quit development, executing the client-side of the utility the usage of JavaScript, querying databases, and model manage structures as well. A full-stack developer provides a price to the corporation and team, owing to growing a various skill-set and the capability to work on a venture independently, thereby decreasing the operational costs. You want to interpret the necessities of the person into the basic structure and put in force it accordingly. You are required to work on each client-side and server-side and recognize the entire manner of utility development. A full-stack developer can swap from one section of a utility to any other besides any problem. You additionally want to sketch the web pages with the usage of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Which technologies are required to become a java full stack developer:
Here is the list of technologies that will help to become a java full-stack developer.
HTML:
CSS
JS
React
Vue
Java
Core Java
JSP-
Servlets
Java Web-service/RestFul API
Hibernate
Spring
Spring boot
Spring security
Spring MVC Testing framework
JUnit
Selenium
Git
1. Backbone
Backbone.js lets you add shape to your JavaScript code. It converts your information into models, which you can control with extra ease. It is notable for creating one-page functions and helps you in maintaining your code equipped and straightforward.
Backbone lets you create customized occasions for your fashions too. And it has a beneficial set of tutorials, which can assist you to get started. It makes updating your code less complicated thru its models.
2. Visual Studio Code
This free and effective device is a necessity if you’re planning to come to be a full-stack developer. VS Code is a supply code editor that is power-packed with several features. It has syntax highlighting, code refactoring, and many different useful aspects that make Visual Studio a must-have.
It is a product of Microsoft, and you can use it with many languages and frameworks, such as JavaScript, Ruby, Rust, etc. Its IntelliSense function provides clever code completion primarily based on the variables, functions, and modules. It additionally allows Git and GitHub integration.
3. CodePen
It is a net improvement surrounding made particularly for internet designers and front-end developers. As a full-stack developer, you have to be educated in each front-end and back-end development. CodePen is the answer for your front-end needs. It has a thriving neighbourhood of front-end builders a place you can share your work.
CodePen makes it simpler for you to construct websites and install them. It helps several frameworks and libraries, which include Vue.js and React. So, you get versatile and supportive improvement surroundings to work in. The interface is convenient to get used to as well.
Its facets let you trade the look of your internet site tons greater shortly and efficiently. Also, you can add new pages without writing new code thanks to its prefill API function.
4. WebStorm
WebStorm is an effective JavaScript IDE. It helps you write JS code with much less effort. WebStorm has a couple of aspects that make the procedure less complicated for the user. Some of its fascinating facets encompass on-the-fly error correction and code completion. These facets assist you in writing code quicker as you make fewer mistakes.
It works with many full stack developer equipment we have stated in this article, consisting of GitHub and Electron. Another interesting function is the definition finder, which lets you discover definitions for something you seem to be for.
The several colour schemes and subject matters make this device exciting to work with. The aid is beneficial, so you don’t face a good deal of trouble in case of trouble arises. For modifying and reviewing, WebStorm is a top-notch choice.
5. TypeScript
TypeScript is a typed superset of Javascript. It compiles to smooth JS, which you can run on any browser or device. As a full-stack developer, you’ll be spending a lot of time writing Javascript code. TypeScript allows you to bring together that code for higher applications. It has more than one facet that assists in static verification of the code as well.
It helps many JS libraries and works on a couple of platforms. TypeScript is open-source, so it’s constantly getting new updates which make it even smoother and more efficient.
You’ll be using it usually for growing giant applications.
6. Slack
Slack is a must-have for full-stack developers. It’s a conversation tool, which is extensively widespread amongst corporations as it simplifies their organization. Slack lets you create workplaces, the place you can chat with your crew participants about unique projects.
It streamlines conversation so you can correctly work with your group members. As a full-stack developer, you’ll be working with a lot of teams. Being acquainted with Slack will assist you in preserving your verbal exchange pristine.
7. GitHub
Over two million organizations use GitHub for development. It is an improvement platform that helps groups in participating in initiatives in real-time. You can use it to host code as well. With real-time collaboration enabled, you can work with different builders and programmers in your group except to deal with confusion.
It mitigates error and makes the technique of writing code extra manageable. Microsoft offered this device recently, and it’s been used with the aid of some of the largest agencies in the world, inclusive of PayPal and IBM.
GitHub has its market of apps and APIs that can make your duties easier. It has a fantastic neighbourhood of builders too, who can assist you in case any confusion arises.
8. Electron
Electron is a framework that lets you create computing device apps by way of the usage of CSS, HTML, and JavaScript. You can boost cross-platform apps with this tool. It’s a Git product and is pretty well-known for app development. Discord and Skype are two first-rate merchandise that had been developed through the usage of the Electron. If you understand net development, you’ll effortlessly be in a position to build laptop purposes with Electron. They launch ordinary updates to repair bugs and enhance personal experience.
0 notes
Text
Spring Boot VS Spring Framework: Razor-Sharp Web Applications
Quick summary:
What comes first- Chicken or the Egg? Something on similar note Spring Boot Vs Sping Framework. Though the framework came earlier, but Spring Boot has taken over with no configuration mess. In this blog, we will help you clear out on the basic concepts, differences, and the unique features of both these frameworks, so that you can analyze what is right for your project plans.
Do share how useful you find this piece of content in the comments below.
Introduction
Looking back at last few years, the Spring framework has become quite complex due to added functionalities. As a result, it takes enormous time and lengthy processes to start a new Spring project. However, to cut down the extra time and effort, Spring Boot was introduced. Using Spring framework as a foundation, Spring Boot is becoming the most preferred framework lately. The question: Spring Boot vs Spring, which is better, still hovers on the mind of many developers.
That said, you might be intrigued by questions like what Spring Boot is and their goals? How is Spring Framework vs Spring Boot different, and how can we compare them? This guide states the basics and Spring Boot vs Spring Framework difference, along with their features and advantages. The guide also states how spring Boot has solved the problems faced with spring. By the end of this guide, you will get precise knowledge about choosing Spring Boot over the spring framework. Straightaway, let’s get started with the Spring VS Spring Boot discussion in detail!
Spring Framework

Spring is a lightweight open-source framework that enables Java EE7 developers to develop reliable, scalable, and simple enterprise applications. It is one of the widely used Java Frameworks to build applications. When it comes to the Java platform, Spring offers an exclusive programming and configuration model.
This framework aims to offer multiple ways to assist you in handling your business objects by simplifying the Java EE development and helping developers be more productive. Spring considers the current business needs and works on fulfilling them.
With Spring, the development of web applications has become quite easy as compared to the classic Application Programming Interfaces(APIs) and Java frameworks like JavaServer Pages(JSP), Java Database Connectivity(JDBC), and Java Servlets. Spring framework adopts new techniques like Plain Old Java Object(POJO), Aspect-Oriented Programming(AOP), and Dependency Injection(DI) to build enterprise applications.
In other terms, the Spring Framework can also be referred to as a set of sub-frameworks or layers like Spring AOP, Spring Web Flow, Spring ORM(object-relational mapping), and Spring Web MVC. These modules collectively can offer better functionalities for a web application.
Benefits Of Spring Framework
Quite a lightweight framework considering the POJO model
Supports Declarative programming
Supports both annotation and XML configurations
Offers middleware services
Enables easy testability and loose coupling
Eliminates the formation of factory classes and singleton.
Best Features Of Spring Framework
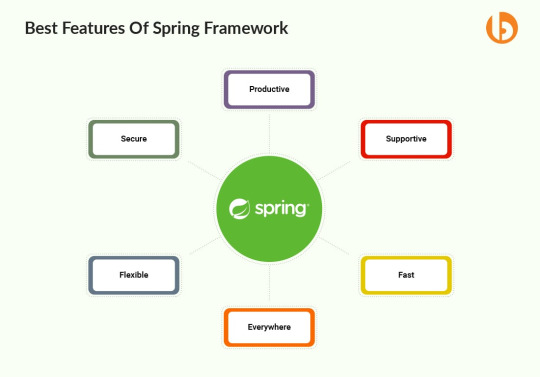
The Spring Framework has several features that are disintegrated into 20 modules to solve several problems. A few more popular Spring Modules include,
Spring JDBC
Spring MVC
Spring ORM
Spring Test
Spring AOP
Spring JMS
Spring Expression Language(SpEL)
Dissimilar to other frameworks, Spring works on specific areas of any application. One chief feature of Spring is the dependency injection. The dependency injection helps to make things simpler by enabling developers to build loosely coupled applications.
Having said that, despite having multiple benefits to offer, why should you choose Spring Boot? To be more precise, what led to the introduction of Spring Boot?
Read More: How Spring Boot Emerged?
0 notes
Text
Spring Boot VS Spring Framework: Razor-Sharp Web Applications
Looking back at last few years, the Spring framework has become quite complex due to added functionalities. As a result, it takes enormous time and lengthy processes to start a new Spring project. However, to cut down the extra time and effort, Spring Boot was introduced. Using Spring framework as a foundation, Spring Boot is becoming the most preferred framework lately. The question: Spring Boot vs Spring, which is better, still hovers on the mind of many developers.
That said, you might be intrigued by questions like what Spring Boot is and their goals? How is Spring Framework vs Spring Boot different, and how can we compare them? This guide states the basics and Spring Boot vs Spring Framework difference, along with their features and advantages. The guide also states how spring Boot has solved the problems faced with spring. By the end of this guide, you will get precise knowledge about choosing Spring Boot over the spring framework. Straightaway, let’s get started with the Spring VS Spring Boot discussion in detail!
Spring Framework
Spring is a lightweight open-source framework that enables Java EE7 developers to develop reliable, scalable, and simple enterprise applications. It is one of the widely used Java Frameworks to build applications. When it comes to the Java platform, Spring offers an exclusive programming and configuration model.
This framework aims to offer multiple ways to assist you in handling your business objects by simplifying the Java EE development and helping developers be more productive. Spring considers the current business needs and works on fulfilling them.
With Spring, the development of web applications has become quite easy as compared to the classic Application Programming Interfaces(APIs) and Java frameworks like JavaServer Pages(JSP), Java Database Connectivity(JDBC), and Java Servlets. Spring framework adopts new techniques like Plain Old Java Object(POJO), Aspect-Oriented Programming(AOP), and Dependency Injection(DI) to build enterprise applications.
In other terms, the Spring Framework can also be referred to as a set of sub-frameworks or layers like Spring AOP, Spring Web Flow, Spring ORM(object-relational mapping), and Spring Web MVC. These modules collectively can offer better functionalities for a web application.
Benefits Of Spring Framework
Quite a lightweight framework considering the POJO model
Supports Declarative programming
Supports both annotation and XML configurations
Offers middleware services
Enables easy testability and loose coupling
Eliminates the formation of factory classes and singleton.
Best Features Of Spring Framework
The Spring Framework has several features that are disintegrated into 20 modules to solve several problems. A few more popular Spring Modules include,
Spring JDBC
Spring MVC
Spring ORM
Spring Test
Spring AOP
Spring JMS
Spring Expression Language(SpEL)
Dissimilar to other frameworks, Spring works on specific areas of any application. One chief feature of Spring is the dependency injection. The dependency injection helps to make things simpler by enabling developers to build loosely coupled applications.
Having said that, despite having multiple benefits to offer, why should you choose Spring Boot? To be more precise, what led to the introduction of Spring Boot?
How Spring Boot Emerged?
With the help of Spring Boot, you can simplify and use the Spring framework easily. While Spring offers loosely coupled applications, it becomes a tedious and difficult task to keep track of the loosely coupled blocks. This is exactly where Spring Boot comes to play.
With the Spring architecture becoming complicated day by day, introducing Spring Boot was necessary. To begin a new project in Spring involves varied processes. When you want to build a Spring framework app, multiple similar configurations need to apply manually. Consequently, it needs to specify frameworks that are to be used and select compatible versions as well. Hence, Spring developers introduced a new framework known as the Spring Boot.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot is built over the Spring framework. Hence, it offers all the features of spring. Spring Boot is a microservice-based framework that enables you to build your app in a shorter time. Each element in Spring Boot is auto-configured. Developers simply need to use accurate configuration to use certain functionality. In case you wish to develop REST API, Spring Boot is highly recommended!
Besides offering utmost flexibility, Spring Boot focuses on shortening the code length, providing you with the easiest method to build a Web application. Featuring default codes and annotation configuration, this framework reduces the time taken to develop an application. In other words, Spring Boot helps to build a stand-alone application with almost zero configuration.
Benefits Of Spring Boot
It does not need XML configuration
It builds stand-alone applications
Compared to Spring, Spring Boot is easier to launch
Spring Boot does not ask you to deploy WAR files
It focuses on reducing the LOC
It helps to embed Jetty, Undertow, or Tomcat directly
Offers easy management and customization
Provides production-ready features.
Spring Boot is typically an extension of Spring Framework that removes the boilerplate configurations needed to set up a fast and efficient Spring application.
Best Features Of Spring Boot
A few features of Spring Boot include,
Embedded server to eliminate complexities in application development
Opinionated starter dependencies to ease the build and app configuration
Auto-configuration for Spring functionality: A chief feature that configures the class based on a specific requirement automatically. It saves you from noting lengthy codes and avoid unnecessary configuration
Health check, metrics, and externalized configuration.
Spring Boot Starter Dependencies
Spring Boot offers a range of starter dependencies for distinct spring modules. Some of the common starter dependencies that allow easy integration include,
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
spring-boot-starter-security
spring-boot-starter-test
spring-boot-starter-web
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
What Makes Spring Boot So Popular?
To answer this question, the first point to be noted is that Spring Boot is based on Java. Java being the most popular programming language globally, there is no doubt why Spring Boot is gaining popularity. Besides this, Spring Boot helps you build an application quickly without worrying about the accuracy and safety of the configuration.
Spring Boot has a vast user community. This further denotes that you can easily find learning courses and materials. Spring Boot is further useful while performing repetitive or long operations.
Advantages Of Spring Boot Over Spring: Spring VS Spring Boot
A few additional benefits include,
Assists in autoconfiguration of all components for a production-grade Spring application
Increases the efficiency of the developmental team
Eliminates manual work that includes annotations, complicated XML configurations, and boilerplate code
Creates and tests Java-based apps by offering a default setup for integration and unit tests
Features embedded HTTP serves such as Tomcat and Jetty to test applications
Offers great admin support. You can handle and monitor through remote access to the application.
Enables easy connecting with queue services and databases such as Redis, Oracle, MySQL, ElasticSearch, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, ActiveMQ, Solr, Rabbit MQ, etc
Integration of Spring Boot with spring ecosystem is easy
Provides flexibility in configuring Database Transaction, Java Beans, and XML configurations
Simplifies the dependency
Tags an embedded Servlet Container along with it
Default configurations allow faster application bootstrapping
Spring Boot does not require a deployment descriptor like the Spring framework.
Read More: Why Choose Spring Boot Over Spring Framework?
0 notes
Text
qaa
https://dzone.com/articles/spring-boot-security-json-web-tokenjwt-hello-world https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/devops/deploying-a-spring-boot-application-on-aws-using-aws-elastic-beanstalk/ https://medium.com/@james.tran/how-to-deploy-spring-boot-2-x-apps-on-websphere-8-5-5-d0b2e257f606 StringBuilder is a mutable sequence of characters. StringBuilder is used when we want to modify Java strings in-place. StringBuilder has methods such as append() , insert() , or replace() that allow to modify strings. ...Jul 6, 2020 Realtek https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41719142/how-to-return-a-set-of-objects-with-spring-boot one-to-many relationship, one record in a table can be associated with one or more records in another table. For example, each customer can have many sales orders. In this example the primary key field in the Customers table, Customer ID, is designed to contain unique values. .... a composite key, you can use the EmbeddedId or the IdClass annotations. I know this question is not strictly about JPA but the rules defined by the specification also applies. So here they are: 2.1.4 Primary Keys and Entity Identity ... A composite primary key must correspond to either a single persistent field or property or to a set of such fields or properties as described below. A primary key class must be defined to represent a composite primary key. Composite primary keys typically arise when mapping from legacy databases when the database key is comprised of several columns. The EmbeddedId and IdClass annotations are used to denote composite primary keys. See sections 9.1.14 and 9.1.15 https://www.yawintutor.com/autowired-injecting-arrays-and-collections-in-spring-boot/ var declarations are globally scoped or function scoped while let and const are block scoped. var variables can be updated and re-declared within its scope; let variables can be updated but not re-declared; const variables can neither be updated nor re-declared .... https://mkyong.com/spring/spring-aop-transaction-management-in-hibernate/ https://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-auto-configuration Arrow functions were introduced in ES6. Arrow functions allow us to write shorter function syntax: Before: Arrow functions were introduced in ES6. Arrow functions allow us to write shorter function syntax: Before: https://www.javatpoint.com/spring-vs-spring-boot-vs-spring-mvc#:~:text=Spring%20Boot%20is%20a%20module%20of%20Spring%20for%20packaging%20the,framework%20under%20the%20Spring%20framework.&text=It%20provides%20ready%20to%20use,need%20to%20build%20configuration%20manually. Endpoint for list of employees https://www.javainuse.com/spring/SpringBoot_DataJPA https://spring.io/guides/tutorials/bookmarks/ observables and promises help us work with asynchronous functionality in JavaScript. Promises deal with one asynchronous event at a time, while observables handle a sequence of asynchronous events over a period of time. Let's see the difference between these two. Emit multiple values over a period of time https://spring.io/guides/gs/consuming-rest-angularjs/ https://www.tutorialspoint.com/angular4/angular4_services.htm https://www.tutorialspoint.com/angular4/angular4_services.htm https://howtodoinjava.com/spring-boot2/rest/rest-api-example/ https://malcoded.com/posts/angular-fundamentals-services/
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP SPRING Interview Questions and Answers
SPRING Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Spring? Spring is an open source development framework for Enterprise Java. The core features of the Spring Framework can be used in developing any Java application, but there are extensions for building web applications on top of the Java EE platform. Spring framework targets to make Java EE development easier to use and promote good programming practice by enabling a POJO-based programming model. 2. What are benefits of Spring Framework? Lightweight: Spring is lightweight when it comes to size and transparency. The basic version of spring framework is around 2MB. Inversion of control (IOC): Loose coupling is achieved in Spring, with the Inversion of Control technique. The objects give their dependencies instead of creating or looking for dependent objects. Aspect oriented (AOP): Spring supports Aspect oriented programming and separates application business logic from system services. Container: Spring contains and manages the life cycle and configuration of application objects. MVC Framework: Spring’s web framework is a well-designed web MVC framework, which provides a great alternative to web frameworks. Transaction Management: Spring provides a consistent transaction management interface that can scale down to a local transaction and scale up to global transactions (JTA). Exception Handling: Spring provides a convenient API to translate technology-specific exceptions (thrown by JDBC, Hibernate, or JDO) into consistent, unchecked exceptions. 3. Which are the Spring framework modules? There are around 20 modules which are generalized into Core Container, Data Access/Integration, Web, AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming), Instrumentation and Test. The basic modules of the Spring framework are : Spring Core Container This layer is basically the core of Spring Framework. It contains the following modules: Core module Bean module Context module Expression Language module Data Access/Integration This layer provides support to interact with the database. It contains the following modules: JDBC module Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) module Java Messaging Service (JMS) module Object XML Mappers (OXM) module Transaction Management module Web This layer provides support to create web application. It contains the following modules: Web module Web-MVC module Web-Socket module Web-Portlet module Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP) In this layer you can use Advices, Pointcuts etc., to decouple the code. Instrumentation – This layer provides support to class instrumentation and classloader implementations. Test This layer provides support to testing with JUnit and TestNG. Messaging This module provides support for STOMP. It also supports an annotation programming model that is used for routing and processing STOMP messages from WebSocket clients. Aspects This module provides support to integration with AspectJ. 4. Explain the Core Container (Application context) module This is the basic Spring module, which provides the fundamental functionality of the Spring framework. BeanFactory is the heart of any spring-based application. Spring framework was built on the top of this module, which makes the Spring container. 5. BeanFactory implementation example A BeanFactory is an implementation of the factory pattern that applies Inversion of Control to separate the application’s configuration and dependencies from the actual application code. The most commonly used BeanFactory implementation is the XmlBeanFactory class. 6. XMLBeanFactory The most useful one is org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory, which loads its beans based on the definitions contained in an XML file. This container reads the configuration metadata from an XML file and uses it to create a fully configured system or application. 7. Explain the AOP module The AOP module is used for developing aspects for our Spring-enabled application. Much of the support has been provided by the AOP Alliance in order to ensure the interoperability between Spring and other AOP frameworks. This module also introduces metadata programming to Spring. 8. Explain the JDBC abstraction and DAO module With the JDBC abstraction and DAO module we can be sure that we keep up the database code clean and simple, and prevent problems that result from a failure to close database resources. It provides a layer of meaningful exceptions on top of the error messages given by several database servers. It also makes use of Spring’s AOP module to provide transaction management services for objects in a Spring application. 9. Explain the object/relational mapping integration module Spring also supports for using of an object/relational mapping (ORM) tool over straight JDBC by providing the ORM module. Spring provides support to tie into several popular ORM frameworks, including Hibernate, JDO, and iBATIS SQL Maps. Spring’s transaction management supports each of these ORM frameworks as well as JDBC. 10. Explain the web module The Spring web module is built on the application context module, providing a context that is appropriate for web-based applications. This module also contains support for several web-oriented tasks such as transparently handling multipart requests for file uploads and programmatic binding of request parameters to your business objects. It also contains integration support with Jakarta Struts.

SPRING Interview Questions 11. Explain the Spring MVC module MVC framework is provided by Spring for building web applications. Spring can easily be integrated with other MVC frameworks, but Spring’s MVC framework is a better choice, since it uses IoC to provide for a clean separation of controller logic from business objects. With Spring MVC you can declaratively bind request parameters to your business objects. 12. Spring configuration file Spring configuration file is an XML file. This file contains the classes information and describes how these classes are configured and introduced to each other. 13. How can we have multiple Spring configuration files? web.xml contextConfigLocation: you can load them all into your Web application context via the ContextConfigLocation element. You’re already going to have your primary applicationContext here, assuming you’re writing a web application. All you need to do is put some white space between the declaration of the next context. applicationContext.xml import resource: you can add your primary applicationContext.xml to the web.xml and then use import statements in that primary context. 14. What are the common implementations of the ApplicationContext? The FileSystemXmlApplicationContext container loads the definitions of the beans from an XML file. The full path of the XML bean configuration file must be provided to the constructor. The ClassPathXmlApplicationContext container also loads the definitions of the beans from an XML file. Here, you need to set CLASSPATH properly because this container will look bean configuration XML file in CLASSPATH. The WebXmlApplicationContext: container loads the XML file with definitions of all beans from within a web application. 15. What is the difference between Bean Factory and ApplicationContext? Application contexts provide a means for resolving text messages, a generic way to load file resources (such as images), they can publish events to beans that are registered as listeners. In addition, operations on the container or beans in the container, which have to be handled in a programmatic fashion with a bean factory, can be handled declaratively in an application context. The application context implements MessageSource, an interface used to obtain localized messages, with the actual implementation being pluggable. 16. What are some of the best practices for Spring Framework? Some of the best practices for Spring Framework are: Define singleton beans with names same as their class or interface names Place Spring bean configuration files under a folder instead of root folder Give common prefixes or suffixes to Spring bean configuration files Avoid using import elements within Spring XML configuration files as much as possible Stay away from auto wiring in XML based bean configurations Always externalize bean property values with property placeholders Select default version-less XSD when importing namespace definitions Always place classpath prefix in resource paths Create a setter method even though you use field level auto wiring Create a separate service layer even though service methods barely delegate their responsibilities to corresponding DAO methods 17. What are the various ways of using Spring Framework? You can use Spring Framework: for writing web applications for exposing RESTful services to secure your web applications for communicating with databases for handling long running jobs to handle external resources or systems you have to work with for testing purposes for standalone java projects to convert your application into an executable to integrate Social Media into your applications 18. How can we use Spring to create Restful Web Service returning JSON response? Any Spring @RestController in a Spring Boot application should render JSON response by default as long as Jackson2 is on the classpath. 19. Spring vs Spring MVC vs Spring Boot? Spring: the most important feature of Spring is Dependency Injection or Inversion of Control. Spring MVC: is a complete HTTP oriented MVC framework managed by the Spring Framework and based in Servlets. It would be equivalent to JSF in the JavaEE stack. Spring Boot: is a utility for setting up applications quickly, offering an out of the box configuration in order to build Spring powered applications. 20. What does a Spring application look like? Interface: An interface that defines the functions. Bean class: It contains properties, its setter and getter methods, functions etc. Spring AOP: Provides the functionality of cross-cutting concerns. The configuration XML file: Contains the information of classes and how to configure them. The Client program: uses the function. Dependency Injection 21. What is Spring IoC container? The Spring IoC is responsible for creating the objects,managing them with dependency injection (DI), wiring them together, configuring them, as also managing their complete lifecycle. 22. What are the benefits of IOC? IOC or dependency injection minimizes the amount of code in an application. It makes easy to test applications, since no singletons or JNDI lookup mechanisms are required in unit tests. Loose coupling is promoted with minimal effort and least intrusive mechanism. IOC containers support eager instantiation and lazy loading of services. 23. How many types of IOC containers are there in spring? BeanFactory: A BeanFactory is essentially nothing more than the interface for an advanced factory capable of maintaining a registry of different beans and their dependencies. The BeanFactory enables you to read bean definitions and access them using the bean factory. ApplicationContext: The ApplicationContext is the central interface within a Spring application for providing configuration information to the application. It is read-only at run time, but can be reloaded if necessary and supported by the application. A number of classes implement the ApplicationContext interface, allowing for a variety of configuration options and types of applications. 24. BeanFactory vs ApplicationContext Application Context: Bean instantiation/wiring Automatic BeanPostProcessor registration Automatic BeanFactoryPostProcessor registration Convenient MessageSource access (for i18n) ApplicationEvent publication BeanFactor: Bean instantiation/wiring 25. What is Dependency Injection in Spring? Dependency Injection, an aspect of Inversion of Control (IoC), is a general concept, and it can be expressed in many different ways.This concept says that you do not create your objects but describe how they should be created. You don’t directly connect your components and services together in code but describe which services are needed by which components in a configuration file. A container (the IOC container) is then responsible for hooking it all up. 26. What is the difference between Tight Coupling and Loose Coupling? Tight Coupling: Tight coupling is when a group of classes are highly dependent on one another. Loose Coupling: Loose coupling is achieved by means of a design that promotes single-responsibility and separation of concerns. 27. What are the different types of IoC (dependency injection)? Constructor-based dependency injection: Constructor-based DI is accomplished when the container invokes a class constructor with a number of arguments, each representing a dependency on other class. Setter-based dependency injection: Setter-based DI is accomplished by the container calling setter methods on your beans after invoking a no-argument constructor or no-argument static factory method to instantiate your bean. 28. Which DI would you suggest Constructor-based or setter-based DI? You can use both Constructor-based and Setter-based Dependency Injection. The best solution is using constructor arguments for mandatory dependencies and setters for optional dependencies. 29. What are Spring beans? The Spring Beans are Java Objects that form the backbone of a Spring application. They are instantiated, assembled, and managed by the Spring IoC container. These beans are created with the configuration metadata that is supplied to the container, for example, in the form of XML definitions. Beans defined in spring framework are singleton beans. There is an attribute in bean tag named "singleton" if specified true then bean becomes singleton and if set to false then the bean becomes a prototype bean. By default it is set to true. So, all the beans in spring framework are by default singleton beans. 30. What does a Spring Bean definition contain? A Spring Bean definition contains all configuration metadata which is needed for the container to know how to create a bean, its lifecycle details and its dependencies. 31. How do you provide configuration metadata to the Spring Container? There are three important methods to provide configuration metadata to the Spring Container: XML based configuration file. Annotation-based configuration Java-based configuration 32. How do you define the scope of a bean? When defining a in Spring, we can also declare a scope for the bean. It can be defined through the scope attribute in the bean definition. For example, when Spring has to produce a new bean instance each time one is needed, the bean’s scope attribute to be prototype. On the other hand, when the same instance of a bean must be returned by Spring every time it is needed, the the bean scope attribute must be set to singleton. 33. Explain the bean scopes supported by Spring There are five scoped provided by the Spring Framework supports following five scopes: In singleton scope, Spring scopes the bean definition to a single instance per Spring IoC container. In prototype scope, a single bean definition has any number of object instances. In request scope, a bean is defined to an HTTP request. This scope is valid only in a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext. In session scope, a bean definition is scoped to an HTTP session. This scope is also valid only in a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext. In global-session scope, a bean definition is scoped to a global HTTP session. This is also a case used in a web-aware Spring ApplicationContext. The default scope of a Spring Bean is Singleton. 34. Are Singleton beans thread safe in Spring Framework? No, singleton beans are not thread-safe in Spring framework. 35. Explain Bean lifecycle in Spring framework The spring container finds the bean’s definition from the XML file and instantiates the bean. Spring populates all of the properties as specified in the bean definition (DI). If the bean implements BeanNameAware interface, spring passes the bean’s id to setBeanName() method. If Bean implements BeanFactoryAware interface, spring passes the beanfactory to setBeanFactory() method. If there are any bean BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, Spring calls postProcesserBeforeInitialization() method. If the bean implements IntializingBean, its afterPropertySet() method is called. If the bean has init method declaration, the specified initialization method is called. If there are any BeanPostProcessors associated with the bean, their postProcessAfterInitialization() methods will be called. If the bean implements DisposableBean, it will call the destroy() method. 36. Which are the important beans lifecycle methods? Can you override them? There are two important bean lifecycle methods. The first one is setup which is called when the bean is loaded in to the container. The second method is the teardown method which is called when the bean is unloaded from the container. The bean tag has two important attributes (init-method and destroy-method) with which you can define your own custom initialization and destroy methods. There are also the correspondive annotations(@PostConstruct and @PreDestroy). 37. What are inner beans in Spring? When a bean is only used as a property of another bean it can be declared as an inner bean. Spring’s XML-based configuration metadata provides the use of element inside the or elements of a bean definition, in order to define the so-called inner bean. Inner beans are always anonymous and they are always scoped as prototypes. 38. How can you inject a Java Collection in Spring? Spring offers the following types of collection configuration elements: The type is used for injecting a list of values, in the case that duplicates are allowed. The type is used for wiring a set of values but without any duplicates. The type is used to inject a collection of name-value pairs where name and value can be of any type. The type can be used to inject a collection of name-value pairs where the name and value are both Strings. 39. What is bean wiring? Wiring, or else bean wiring is the case when beans are combined together within the Spring container. When wiring beans, the Spring container needs to know what beans are needed and how the container should use dependency injection to tie them together. 40. What is bean autowiring? The Spring container is able to autowire relationships between collaborating beans. This means that it is possible to automatically let Spring resolve collaborators (other beans) for a bean by inspecting the contents of the BeanFactory without using and elements. 41. Explain different modes of autowiring? The autowiring functionality has five modes which can be used to instruct Spring container to use autowiring for dependency injection: no: This is default setting. Explicit bean reference should be used for wiring. byName: When autowiring byName, the Spring container looks at the properties of the beans on which autowire attribute is set to byName in the XML configuration file. It then tries to match and wire its properties with the beans defined by the same names in the configuration file. byType: When autowiring by datatype, the Spring container looks at the properties of the beans on which autowire attribute is set to byType in the XML configuration file. It then tries to match and wire a property if its type matches with exactly one of the beans name in configuration file. If more than one such beans exist, a fatal exception is thrown. constructor: This mode is similar to byType, but type applies to constructor arguments. If there is not exactly one bean of the constructor argument type in the container, a fatal error is raised. autodetect: Spring first tries to wire using autowire by constructor, if it does not work, Spring tries to autowire by byType. 42. Are there limitations with autowiring? Limitations of autowiring are: Overriding: You can still specify dependencies using and settings which will always override autowiring. Primitive data types: You cannot autowire simple properties such as primitives, Strings, and Classes. Confusing nature: Autowiring is less exact than explicit wiring, so if possible prefer using explicit wiring. 43. Can you inject null and empty string values in Spring? Yes, you can. Spring Annotations 44. What are some of the important Spring annotations? Some of the Spring annotations that I have used in my project are: Component is used to indicate that a class is a component. These classes are used for auto-detection and configured as bean when annotation based configurations are used. Controller is a specific type of component, used in MVC applications and mostly used with @RequestMapping annotation. Repository annotation is used to indicate that a component is used as repository and a mechanism to store/retrieve/search data. We can apply this annotation with DAO pattern implementation classes. Service is used to indicate that a class is a Service. Usually, the business facade classes that provide some services are annotated with this. Required – This annotation simply indicates that the affected bean property must be populated at configuration time, through an explicit property value in a bean definition or through autowiring. The container throws BeanInitializationException if the affected bean property has not been populated. ResponseBody – for sending Object as response, usually for sending XML or JSON data as response. PathVariable – for mapping dynamic values from the URI to handler method arguments. Autowired – provides more fine-grained control over where and how autowiring should be accomplished. It can be used to autowire bean on the setter method just like @Required annotation, on the constructor, on a property or pn methods with arbitrary names and/or multiple arguments. Qualifier – When there are more than one beans of the same type and only one is needed to be wired with a property, the @Qualifier annotation is used along with @Autowired annotation to remove the confusion by specifying which exact bean will be wired. Scope – for configuring scope of the spring bean. Configuration – indicates that the class can be used by the Spring IoC container as a source of bean definitions. ComponentScan – all the classes available under a package will be scanned when this annotation is applied. Bean – for java based configurations, tells spring that a method annotated with @Bean will return an object that should be registered as a bean in the spring application context. AspectJ annotations for configuring aspects and advices, @Aspect, @Before, @After, @Around, @Pointcut etc. 45. What does the @RequestParam annotation do? The @RequestParam annotation in spring binds the parameter values of a query string to the method argument of a controller. 46. What is the importance of the annotation @Primary When there are multiple beans of the same data-type, developers use the Spring-specific @Primary annotation that automatically gives the higher preference to a particular bean. This annotation can be used on any class directly or indirectly annotated with the @Component annotation or on methods annotated with the @Bean annotation. 47. What is the difference between the Configuration types XML and Annotation? Advantages of the annotation: All the information is in a single file When the class changes, no need to modify the xml file Advantages of XML file: Clear separation between the POJO and its behavior When you do not know which POJO is responsible for the behavior, it is easier to find that POJO 48. What is the role of @SpringBootApplication? The @SpringBootApplication annotation was introduced in Spring Boot 1.2.0 and it enables the auto-configuration feature. This annotation encapsulates the working of three different annotations: @Configuration: Allows the developers to explicitly register the beans @ComponentScan: Enables the component-scanning so that the controller class and other components will be automatically discovered and registered as beans in spring’s application context @EnableAutoConfiguration: Enables the auto-configuration feature of spring boot This annotation takes up the following optional parameters: exclude: Excludes the list of classes from the auto-configuration excludeNames: Excludes the list of fully qualified class names from the auto configuration scanBasePackage: Provides the list of packages which must be applied for scanning scanBasePackageClasses: Provides the list of classes in the other package which must be applied for scanning 49. Explain the @InitBinder? This annotation is decorated on a method in which a date format is declared, and throughout the class, the defined date format is used. Whenever the binding happens with a date field @InitBinder; annotation says to use the CustomDateEditor, which in return uses the date format mentioned in @InitBinder. 50. Define @ControllerAdvice? Classes with @ControllerAdvice can be declared explicitly as Spring beans or auto-detected via classpath scanning. All such beans are sorted via AnnotationAwareOrderComparator, i.e. based on @Order and Ordered, and applied in that order at runtime. For handling exceptions, an @ExceptionHandler will be picked on the first advice with a matching exception handler method. For model attributes and InitBinder initialization, @ModelAttribute and @InitBinder methods will also follow @ControllerAdvice order. 51. Can we send an Object as the response of Controller handler method? Yes we can send JSON or XML based response in restful web services, using the @ResponseBody annotation. 52. Explain @ModelAttribute? The @ModelAttribute annotation refers to the property of the Model object and is used to prepare the model data. This annotation binds a method variable or the model object to a named model attribute. The annotation accepts an optional value which indicates the name of the model attribute. The @ModelAttribute annotation can be used at the parameter level or the method level. The use of this annotation at the parameter level is to accept the request form values while at the method level is to assign the default values to a model. Let me explain you further with the help of some examples. 53. @RequestMapping annotation The @RequestMapping annotation is used to map the web request onto a handler class (i.e. Controller) or a handler method and it can be used at the Method Level or the Class Level. If developers use the @RequestMapping annotation at a class level, it will be as a relative path for the method level path. 54. What is Spring Java-Based Configuration? Give some annotation example. Java based configuration option enables you to write most of your Spring configuration without XML but with the help of few Java-based annotations. An example is the @Configuration annotation, that indicates that the class can be used by the Spring IoC container as a source of bean definitions. Another example is the@Bean annotated method that will return an object that should be registered as a bean in the Spring application context. 55. What is Annotation-based container configuration? An alternative to XML setups is provided by annotation-based configuration which relies on the bytecode metadata for wiring up components instead of angle-bracket declarations. Instead of using XML to describe a bean wiring, the developer moves the configuration into the component class itself by using annotations on the relevant class, method, or field declaration. 56. How do you turn on annotation wiring? Annotation wiring is not turned on in the Spring container by default. In order to use annotation based wiring we must enable it in our Spring configuration file by configuring element. Spring Data Access 57. Which classes are present in spring JDBC API? Spring framework provides the following approaches for Jdbc database access: JdbcTemplate SimpleJdbcTemplate NamedParameterJdbcTemplate SimpleJdbcInsert SimpleJdbcCall 58. How can JDBC be used more efficiently in the Spring framework? When using the Spring JDBC framework the burden of resource management and error handling is reduced. So developers only need to write the statements and queries to get the data to and from the database. JDBC can be used more efficiently with the help of a template class provided by Spring framework, which is the JdbcTemplate (example here). 59. JdbcTemplate JdbcTemplate class provides many convenience methods for doing things such as converting database data into primitives or objects, executing prepared and callable statements, and providing custom database error handling. 60. How can you fetch records by spring JdbcTemplate? There are two interfaces that can be used to fetch records from the database: ResultSetExtractor RowMapper 61. What is the advantage of NamedParameterJdbcTemplate? NamedParameterJdbcTemplate is built upon JDBCTemplate which is provided by spring and used for lower level communication with databases. It makes possible to pass SQL query arguments as key value pairs. As a result the program code is much more readable and therefore serves as better documentation compared to the indexed or the “?” placeholder approach. The latter is harder to follow specially if the number of parameters is huge. 62. What is Spring JDBCTemplate class and how to use it? The JdbcTemplate class executes SQL queries, update statements and stored procedure calls, performs iteration over ResultSets and extraction of returned parameter values. It handles the creation and release of resources, thus avoiding errors such as forgetting to close the connection. It also catches JDBC exceptions and translates them to the generic, more informative, exception hierarchy defined in the org.springframework.dao package. 63. What is the difference between JDBC and Spring JDBC? Spring JDBC value-add provided by the Spring Framework’s on top JDBC layer Define connection parameters Open the connection Specify the statement Prepare and execute the statement Set up the loop to iterate through the results (if any) Do the work for each iteration Process any exception Handle transactions Close the connection 64. Spring DAO support The Data Access Object (DAO) support in Spring is aimed at making it easy to work with data access technologies like JDBC, Hibernate or JDO in a consistent way. This allows us to switch between the persistence technologies fairly easily and to code without worrying about catching exceptions that are specific to each technology. 65. What are the ways to access Hibernate by using Spring? There are two ways to access Hibernate with Spring: Inversion of Control with a Hibernate Template and Callback. Extending HibernateDAOSupport and Applying an AOP Interceptor node. 66. ORM’s Spring support Spring supports the following ORM’s: Hibernate iBatis JPA (Java Persistence API) TopLink JDO (Java Data Objects) OJB 67. How can we integrate Spring and Hibernate using HibernateDaoSupport? Use Spring’s SessionFactory called LocalSessionFactory. The integration process is of 3 steps: Configure the Hibernate SessionFactory Extend a DAO Implementation from HibernateDaoSupport Wire in Transaction Support with AOP 68. Types of the transaction management Spring support Spring supports two types of transaction management: Programmatic transaction management: This means that you have managed the transaction with the help of programming. That gives you extreme flexibility, but it is difficult to maintain. Declarative transaction management: This means you separate transaction management from the business code. You only use annotations or XML based configuration to manage the transactions. 69. What are the benefits of the Spring Framework’s transaction management? It provides a consistent programming model across different transaction APIs such as JTA, JDBC, Hibernate, JPA, and JDO. It provides a simpler API for programmatic transaction management than a number of complex transaction APIs such as JTA. It supports declarative transaction management. It integrates very well with Spring’s various data access abstractions. 70. Which Transaction management type is more preferable? Most users of the Spring Framework choose declarative transaction management because it is the option with the least impact on application code, and hence is most consistent with the ideals of a non-invasive lightweight container. Declarative transaction management is preferable over programmatic transaction management though it is less flexible than programmatic transaction management, which allows you to control transactions through your code. Spring Aspect Oriented Programming (AOP) 71. Explain AOP Aspect-oriented programming, or AOP, is a programming technique that allows programmers to modularize crosscutting concerns, or behavior that cuts across the typical divisions of responsibility, such as logging and transaction management. 72. What are the advantages of spring AOP? a. It is non-invasive Your service/domain classes get advised by the aspects (cross cutting concerns) without adding any Spring AOP related classes or interfaces into the service/domain classes. Allows the developer to concentrate on the business code, instead the cross cutting concerns. b. Its implemented in pure Java No need for a special compilation unit, or a special class loader c. It uses Spring’s IOC for dependency injection Aspects can be configured as normal spring beans. d. As any other AOP framework, it weaves cross cutting concerns into the classes, without making a call to the cross cutting concerns from those classes. e. Centralize or modularize the cross cutting concerns Easy to maintain and make changes to the aspects Changes need to be made in one place. In one of your classes you don’t want to have logging, it can easily be achieved by modifying the point cut in the respective aspect (logging aspect). So you need to make changes in only one place. f. Provision to create aspects using schema based (XML configuration) or @AspectJ annotation based style. g. Easy to configure 73. What are the AOP implementation? AOP implementations: Spring AOP: Runtime weaving through proxy is done It supports only method level PointCut It is DTD based Apache AspectJ Compile time weaving through AspectJ Java tools is done It suports field level Pointcuts It is schema based and Annotation configuration JBoss AOP JBoss AOP is not only a framework, but also a prepackaged set of aspects that are applied via annotations, pointcut expressions, or dynamically at runtime. Some of these include caching, asynchronous communication, transactions, security, remoting, and many many more. 74. What are the AOP terminology? Aspect Advice Pointcut JoinPoint Introduction Target Object AOP Proxy Weaving 75. Aspect The core construct of AOP is the aspect, which encapsulates behaviors affecting multiple classes into reusable modules. It ia a module which has a set of APIs providing cross-cutting requirements. For example, a logging module would be called AOP aspect for logging. An application can have any number of aspects depending on the requirement. In Spring AOP, aspects are implemented using regular classes annotated with the @Aspect annotation (@AspectJ style). 76. Join point The join point represents a point in an application where we can plug-in an AOP aspect. It is the actual place in the application where an action will be taken using Spring AOP framework. 77. Advice The advice is the actual action that will be taken either before or after the method execution. This is actual piece of code that is invoked during the program execution by the Spring AOP framework. Spring aspects can work with five kinds of advice: before: Run advice before the a method execution. after: Run advice after the a method execution regardless of its outcome. after-returning: Run advice after the a method execution only if method completes successfully. after-throwing: Run advice after the a method execution only if method exits by throwing an exception. around: Run advice before and after the advised method is invoked. 78. Pointcut The pointcut is a set of one or more joinpoints where an advice should be executed. You can specify pointcuts using expressions or patterns. 79. What is Introduction? An Introduction allows us to add new methods or attributes to existing classes. 80. What is Target object? The target object is an object being advised by one or more aspects. It will always be a proxy object. It is also referred to as the advised object. 81. What is a Proxy? A proxy is an object that is created after applying advice to a target object. When you think of client objects the target object and the proxy object are the same. 82. What are the different types of AutoProxying? BeanNameAutoProxyCreator DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator Metadata autoproxying 83. What is Weaving? What are the different points where weaving can be applied? Weaving is the process of linking aspects with other application types or objects to create an advised object. Weaving can be done at compile time, at load time, or at runtime. 84. What is the difference between concern and cross-cutting concern in Spring AOP The Concern is behavior we want to have in a module of an application. A Concern may be defined as a functionality we want to implement. The cross-cutting concern is a concern which is applicable throughout the application and it affects the entire application. For example, logging, security and data transfer are the concerns which are needed in almost every module of an application, hence they are cross-cutting concerns. 85. Explain XML Schema-based aspect implementation? In this implementation case, aspects are implemented using regular classes along with XML based configuration. 86. Explain annotation-based (@AspectJ based) aspect implementation This implementation case (@AspectJ based implementation) refers to a style of declaring aspects as regular Java classes annotated with Java 5 annotations. Spring Model View Controller (MVC) 87. What is Spring MVC framework? Spring comes with a full-featured MVC framework for building web applications. Although Spring can easily be integrated with other MVC frameworks, such as Struts, Spring’s MVC framework uses IoC to provide a clean separation of controller logic from business objects. It also allows to declaratively bind request parameters to business objects. 88. What are the minimum configurations needed to create Spring MVC application? For creating a simple Spring MVC application, we would need to do the following tasks: Add spring-context and spring-webmvc dependencies in the project. Configure DispatcherServlet in the web.xml file to handle requests through spring container. Spring bean configuration file to define beans, if using annotations then it has to be configured here. Also we need to configure view resolver for view pages. Controller class with request mappings defined to handle the client requests. 89. List out all the concepts that are available in the MVC Architecture? The browser sends a request to DispatcherServlet DispatcherServlet knows the HanderMapping and can find the appropriate controllers Controllers execute the request and put the data in the model and return back the view name to the DispatcherServlet. DispatcherServlet uses the view name and ViewResolver to map to the view. 90. DispatcherServlet The Spring Web MVC framework is designed around a DispatcherServlet that handles all the HTTP requests and responses. 91. WebApplicationContext The WebApplicationContext is an extension of the plain ApplicationContext that has some extra features necessary for web applications. It differs from a normal ApplicationContext in that it is capable of resolving themes, and that it knows which servlet it is associated with. 92. What is Controller in Spring MVC framework? Controllers provide access to the application behavior that you typically define through a service interface. Controllers interpret user input and transform it into a model that is represented to the user by the view. Spring implements a controller in a very abstract way, which enables you to create a wide variety of controllers. 93. How would you relate Spring MVC Framework to MVC architecture? Spring MVC framework: The Spring Framework is an open source application framework and inversion of control container for the Java platform. MVC architecture: Model View Controller (MVC) as it is popularly called, is a software design pattern for developing web applications 94. What is ViewResolver in Spring MVC? Spring provides ViewResolver, which enable you to render models in a browser without tying you to a specific view technology. Out of the box, Spring enables you to use JSPs, Velocity templates and XSLT views, for example. The two interfaces which are important to the way Spring handles views are ViewResolver and View. The ViewResolver provides a mapping between view names and actual views. The View interface addresses the preparation of the request and hands the request over to one of the view technologies. 95. What is a MultipartResolver and when its used? Spring MVC provide multipart support with MultipartResolver. The MultipartResolver parses inbound multipart requests. You can enable multipart support by registering a MultipartResolver bean in the DispatcherServlet application context. 96. How to upload file in Spring MVC Application? Spring provides built-in support for uploading files through MultipartResolver interface implementations. There is also a validator for the field, which will be used to check if the file uploaded is of size greater than zero. There is finally a simple view that contains a form with the option to upload a file. 97. How to validate form data in Spring Web MVC Framework? There are 3 different ways to perform validation : using annotation, manually, or a mix of both. 98. What is Spring MVC Interceptor and how to use it? Spring’s handler mapping mechanism includes handler interceptors, which are useful when you want to apply specific functionality to certain requests, for example, checking for a principal. Interceptors must implement HandlerInterceptor from the org.springframework.web.servlet package. This interface defines three methods: preHandle is called before the actual handler is executed. postHandle is called after the handler is executed. afterCompletion is called after the complete request has finished. Authentication and authorization 99. What is Spring Security? Spring security is one of the most important modules of the Spring framework. It enables the developers to integrate the security features easily and in a managed way. In the following example, we will show how to implement Spring Security in a Spring MVC application. 100. Why Spring Boot? Here are some useful benefits of using Spring Boot: Automatic configuration of an application uses intelligent defaults based on the classpath and the application context, but they can be overridden to suit the developer’s requirements as needed. When creating a Spring Boot Starter project, you select the features that your application needs and Spring Boot will manage the dependencies for you. A Spring Boot application can be packaged as a JAR file. The application can be run as a standalone Java application from the command line using the java -jar command. When developing a web application, Spring Boot configures an embedded Tomcat server so that it can be run as a standalone application. (Tomcat is the default, but you can configure Jetty or Undertow instead.) You can package the application as a WAR file and deploy it to an external servlet container if you prefer Spring Boot includes many useful non-functional features (such as security and health checks) right out of the box. SPRING Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
